Off Grid Living Documentary A Modern Exploration
Off Grid Living Documentary explores the burgeoning movement of individuals choosing self-sufficiency and a disconnect from traditional infrastructure. This documentary delves into the practicalities, challenges, and rewards of a life lived beyond the grid, examining everything from sustainable energy solutions and waste management to the social dynamics and economic considerations of this increasingly popular lifestyle choice. From building self-sufficient homes to navigating the complexities of off-grid living, the film promises a comprehensive and insightful look at a world apart.
The documentary will feature interviews with experienced off-grid dwellers, showcasing their daily routines, innovative technologies, and the unique challenges they overcome. It will also analyze the environmental impact of this lifestyle, comparing it to conventional living and exploring the potential for creating sustainable and resilient communities. Financial aspects, including initial investment costs and long-term economic implications, will also be thoroughly investigated, providing viewers with a realistic understanding of the financial commitments involved.
Defining Off-Grid Living
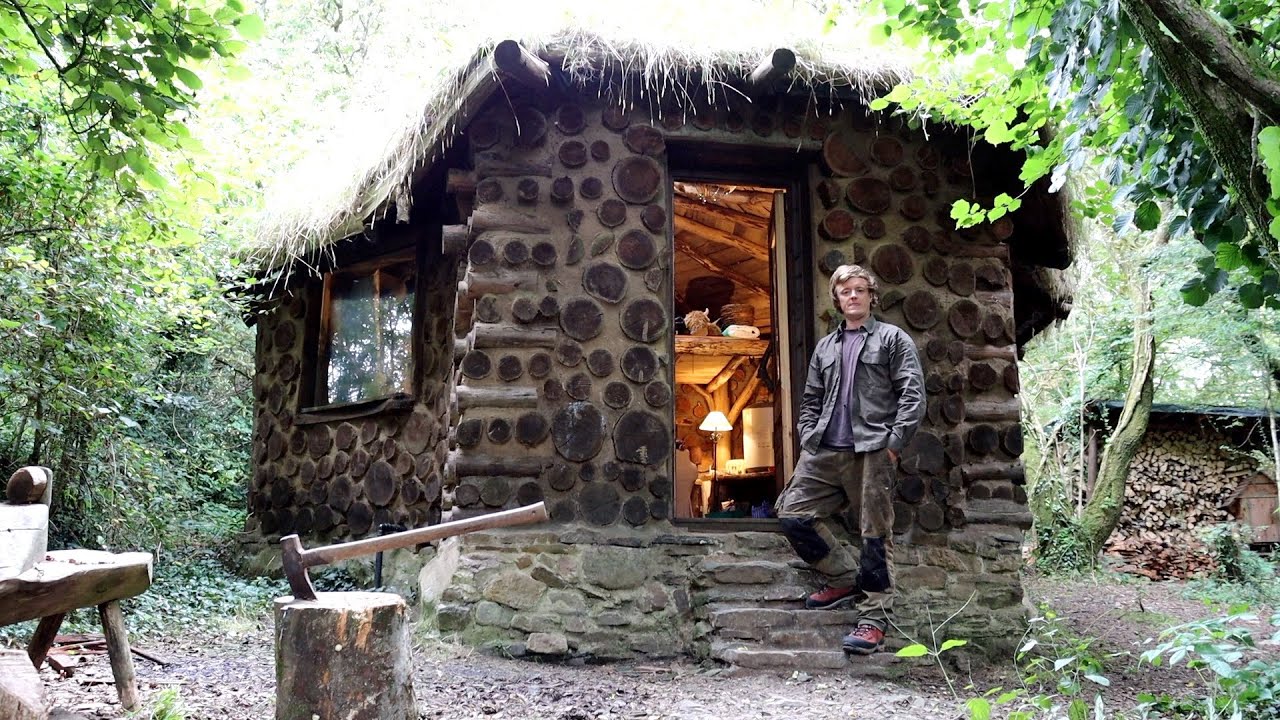
Off-grid living represents a deliberate departure from the conventional reliance on centralized utilities and services. It encompasses a spectrum of lifestyles, all united by a common thread: self-sufficiency and reduced environmental impact. This movement reflects a growing desire for independence, resilience, and a closer connection with nature.Off-grid living is not a monolithic concept; it exists on a continuum, ranging from partial to complete self-sufficiency.
The level of “off-gridness” is determined by the extent to which a household generates its own energy, water, and food, and manages its waste independently.
Levels of Off-Grid Existence
The degree of off-grid living varies considerably. Partial off-grid living might involve using solar panels for electricity but still relying on municipal water and sewer systems. Conversely, complete off-grid living aims for total independence from external infrastructure, often involving rainwater collection, composting toilets, and extensive food production. The choice reflects individual priorities, resources, and geographic location.
Comparison with Traditional Lifestyles
Traditional lifestyles, particularly in pre-industrial societies, often inherently incorporated many aspects of off-grid living. However, modern off-grid living is a conscious choice, often informed by environmental concerns, a desire for simplicity, and a rejection of consumerism. Traditional lifestyles were often dictated by necessity, whereas modern off-grid living is often a deliberate lifestyle choice. While traditional communities might have lacked the technological tools available to modern off-grid dwellers (like solar panels), their practices often mirrored the core principles of sustainability and self-reliance.
A Typical Day in the Life of an Off-Grid Dweller
The daily routine of an off-grid individual varies greatly depending on factors such as location, resources, and personal preferences. However, common themes include a strong emphasis on self-sufficiency and a close relationship with the natural environment. Challenges often revolve around resource management, weather dependency, and the need for constant maintenance and repair of self-built systems.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting what is off grid living today.
| Time of Day | Activity | Resources Used | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6:00 AM | Wake up, collect rainwater for the day’s needs | Rainwater collection system, buckets | Insufficient rainfall, system maintenance |
| 7:00 AM | Tend to livestock, gather eggs | Chickens, goats, pasture land | Predator control, animal health |
| 8:00 AM | Prepare breakfast using homegrown vegetables and solar-cooked eggs | Homegrown vegetables, solar oven, eggs | Cloudy weather reducing solar oven efficiency |
| 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Work on maintaining the solar panel system and water pump | Tools, solar panels, water pump | Technical troubleshooting, part replacement |
| 12:00 PM | Lunch using homegrown produce | Homegrown produce | Crop failure due to pests or weather |
| 1:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Gardening and composting | Gardening tools, compost bin | Pest control, soil fertility management |
| 5:00 PM | Prepare dinner using homegrown ingredients | Homegrown ingredients, wood-burning stove | Gathering firewood, managing stove temperature |
| 7:00 PM | Evening chores, checking security systems | Flashlight, security system | Wildlife encounters, system malfunctions |
| 8:00 PM | Relax and read by solar-powered lamp | Solar-powered lamp, books | Limited access to information and entertainment |
Technological Aspects of Off-Grid Living

Embracing self-sufficiency necessitates a deep understanding and implementation of various technologies. Off-grid living demands resourcefulness and innovation to overcome the challenges of accessing traditional utilities. The successful integration of appropriate technologies is paramount for comfort, safety, and sustainability in these lifestyles.
Energy Generation Technologies
Off-grid communities rely heavily on renewable energy sources. Solar power, harnessing sunlight via photovoltaic (PV) panels, converts light directly into electricity. Wind turbines capture kinetic energy from moving air, converting it into usable electricity. Hydropower utilizes the energy of flowing water, often via small-scale turbines, to generate electricity. The choice of technology depends on the specific location’s resources and energy demands.
System sizing requires careful consideration of energy consumption patterns and the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Battery storage systems are crucial for providing power during periods of low solar irradiance or wind speed.
Water Collection and Purification Methods
Securing a reliable water supply is critical for off-grid survival. Rainwater harvesting, utilizing roof catchment systems and storage tanks, is a common method. Groundwater collection involves drilling wells or utilizing existing springs. Water purification is equally important, employing methods such as boiling, filtration (using sand, gravel, and charcoal filters), and UV sterilization. The selection of a purification method depends on the initial water quality and the level of purification required.
Proper sanitation and hygiene practices are crucial in conjunction with these methods to prevent waterborne illnesses.
Waste Management Strategies
Effective waste management is essential for maintaining a healthy and sustainable off-grid environment. Composting toilets, which decompose human waste organically, are frequently employed. Greywater recycling systems reuse wastewater from showers and sinks for irrigation, conserving water resources. Proper waste sorting and recycling programs are implemented to minimize landfill waste. The emphasis is on minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource reuse, in keeping with the principles of sustainability.
Anaerobic digestion, a process that breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, can also be used to produce biogas for fuel.
Innovative Technologies Enhancing Off-Grid Living
Several innovative technologies are steadily improving the quality of life in off-grid communities.
- Improved Solar Panel Efficiency: Advances in photovoltaic technology have led to higher efficiency solar panels, requiring less space to generate the same amount of power.
- Advanced Battery Storage Systems: Longer-lasting and more efficient battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, are extending the usability of renewable energy sources.
- Smart Home Automation Systems: These systems optimize energy consumption by automating lighting, appliances, and other energy-using devices.
- Water Purification Tablets: Portable and easy-to-use water purification tablets provide a simple and effective method for purifying water in remote locations.
- Off-grid communication systems: Satellite internet and alternative communication technologies provide access to information and connectivity, bridging the gap with the outside world.
Challenges and Rewards of Off-Grid Living: Off Grid Living Documentary
The allure of self-sufficiency and a simpler life draws many to off-grid living, but the reality presents a complex tapestry of challenges and rewards. While the romantic vision often dominates initial interest, the practicalities demand resilience, resourcefulness, and a deep understanding of the commitment involved. This section explores the significant hurdles faced by off-grid dwellers and the profound personal fulfillment that often outweighs the difficulties.
Significant Challenges Faced by Off-Grid Dwellers, Off grid living documentary
Life off the grid presents a unique set of obstacles. The most significant challenges often revolve around resource management, infrastructure limitations, and the psychological adjustments required for a drastic lifestyle shift. These challenges are not insurmountable, but they demand careful planning, adaptability, and a realistic understanding of the commitment involved.
Resource Management and Infrastructure Limitations
Securing reliable access to water, power, and food is paramount. Water sources may be unpredictable, requiring extensive planning for collection, filtration, and storage. Power generation, whether solar, wind, or other means, necessitates technical understanding and maintenance. Food production, whether through gardening or hunting/gathering, demands significant time, effort, and knowledge. Furthermore, the lack of readily available infrastructure necessitates self-reliance in areas such as waste disposal, healthcare, and emergency response.
These factors combine to create a demanding and often unpredictable lifestyle.
Psychological and Emotional Impacts of Off-Grid Living
The transition to off-grid living significantly impacts psychological and emotional well-being. While some thrive on the increased independence and connection with nature, others struggle with isolation, the constant demands of self-sufficiency, and the lack of readily available social interaction. The emotional toll can be substantial, particularly during periods of hardship or unexpected setbacks. Conversely, the sense of accomplishment and connection with nature can provide significant emotional rewards, fostering resilience and a profound sense of self-reliance.
Personal Stories Illustrating the Difficulties and Joys of Off-Grid Living
Sarah, a former software engineer, traded her cubicle for a cabin in the woods. Initially, the peace and quiet were idyllic. However, a harsh winter brought unexpected challenges. A frozen water pipe left her without running water for days, a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in off-grid living. Despite this, she found immense satisfaction in mastering new skills, such as wood-splitting and basic plumbing repair, and a deeper appreciation for the resilience of the human spirit.
Mark, a retired teacher, and his wife, Susan, built their dream off-grid home on a remote mountainside. While they faced numerous technical challenges, including mastering solar power and rainwater harvesting, their greatest joy came from the close-knit community they fostered with their neighbors. Regular barbecues and shared harvests fostered strong bonds and a sense of belonging, proving that even in isolation, connection is possible.
Personal Rewards and Fulfillment Derived from Off-Grid Living
The rewards of off-grid living are often deeply personal and profoundly transformative. The increased self-reliance and problem-solving skills developed are invaluable. The direct connection with nature fosters a deep appreciation for the environment and a simpler way of life. Many off-grid dwellers report a significant improvement in their mental and physical health, attributed to reduced stress, increased physical activity, and a stronger sense of purpose.
The profound sense of accomplishment and independence is a powerful motivator for many who choose this lifestyle.
Ultimately, Off Grid Living Documentary offers a nuanced perspective on a lifestyle that is both alluring and demanding. It showcases the ingenuity and resilience of those who embrace off-grid living, highlighting the personal rewards and the ongoing challenges they face. By presenting both the romantic ideal and the practical realities, the documentary provides viewers with a comprehensive and thought-provoking exploration of a growing movement and its potential impact on the future.