How To Make Money Off-Grid Living
How to make money off grid living – How to make money off-grid living unveils the secrets to a financially fulfilling and environmentally conscious lifestyle. Escape the 9-to-5 grind and embrace self-sufficiency, discovering innovative ways to generate income while living in harmony with nature. This isn’t just a guide; it’s a blueprint for a richer, more independent life, exploring sustainable energy solutions, profitable off-grid businesses, and savvy financial strategies to ensure your success.
Prepare to embark on a journey towards a life less ordinary, one where financial freedom and environmental responsibility intertwine seamlessly.
From harnessing the power of the sun and wind to cultivating your own food and crafting unique goods, we’ll delve into practical methods for generating income while minimizing your environmental impact. We’ll explore diverse business models, address the challenges of off-grid living, and provide actionable steps to help you build a thriving and sustainable future. Learn how to leverage your skills, build a strong online presence, and navigate the financial aspects of this exciting lifestyle change.
Generating Income Off-Grid
Embracing off-grid living often necessitates a shift in mindset, requiring ingenuity and resourcefulness to generate income sustainably. This involves leveraging the very environment you’ve chosen to inhabit, harnessing its natural resources to create both a livelihood and a self-sufficient lifestyle. This section will explore various methods of generating income while minimizing your environmental footprint.
Renewable Energy Systems for Off-Grid Income Generation
Generating your own electricity is fundamental to off-grid living, and this can also become a source of income. Several renewable energy options exist, each with its own set of advantages, disadvantages, and associated costs. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about your energy system and its potential to generate revenue.
Cost Breakdown of Off-Grid Energy Systems
The initial investment for a sustainable off-grid energy system varies significantly based on factors such as location, energy needs, and chosen technology. A basic solar system for a small cabin might cost between $5,000 and $15,000, while a more comprehensive system for a larger home or business could easily exceed $50,000. This includes the cost of solar panels, batteries, inverters, wiring, and installation.
Wind turbines represent a higher initial investment, often starting at $10,000 and increasing substantially with turbine size and capacity. Hydropower systems are typically the most expensive option, requiring significant engineering and infrastructure, with costs often reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars. These costs can be offset, however, through government incentives, grants, and tax credits available in many regions.
Examples of Successful Off-Grid Businesses
Many successful businesses thrive entirely off-grid, demonstrating the viability of this lifestyle. Consider eco-lodges in remote areas powered by solar energy, offering unique and sustainable tourism experiences. These businesses not only generate income but also promote environmental consciousness. Similarly, farms utilizing solar-powered irrigation systems can produce organic produce for local markets, creating both food security and financial stability.
Small-scale craft businesses, powered by renewable energy, can produce and sell handcrafted goods online, reaching a wider customer base. The key is to identify a niche market and leverage renewable energy to minimize operational costs and maximize profit margins.
Comparison of Solar, Wind, and Hydro Power
| Feature | Solar Power | Wind Power | Hydro Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate to High (depending on scale) | High | Very High |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate to High | Moderate to High |
| Reliability | Dependent on sunlight; requires battery storage | Dependent on wind speed; requires battery storage | Highly reliable, but requires consistent water flow |
| Environmental Impact | Low | Moderate (impact on birds and bats) | Moderate to High (depending on dam size and location) |
Off-Grid Agriculture and Food Production
Embracing self-sufficiency in an off-grid lifestyle necessitates a deep understanding of sustainable food production. Successfully cultivating your own food provides not only nourishment but also significant cost savings and a stronger connection to the land. This section explores various strategies for thriving in an off-grid agricultural setting, addressing challenges and highlighting successful approaches.
Sustainable off-grid agriculture requires careful planning and adaptation to your specific environment. Factors such as climate, soil type, and available water resources significantly influence your choices. The key lies in maximizing efficiency and minimizing reliance on external inputs, prioritizing resilience and long-term sustainability.
Hydroponics and Aquaponics Systems
Hydroponics, the cultivation of plants in nutrient-rich water without soil, and aquaponics, which integrates hydroponics with aquaculture (raising fish), offer highly efficient methods for off-grid food production. Hydroponic systems, utilizing techniques like deep water culture or nutrient film technique, allow for year-round cultivation regardless of soil conditions. Aquaponics leverages the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants; fish waste provides nutrients for plants, while plants filter the water for the fish.
This closed-loop system minimizes water usage and waste, creating a remarkably self-sustaining food production unit. A well-designed aquaponic system can provide a consistent supply of fish and vegetables, significantly enhancing food security in an off-grid setting. For example, a small-scale aquaponics system in a temperate climate might successfully cultivate lettuce, tomatoes, and tilapia.
Challenges of Maintaining Food Security Off-Grid and Potential Solutions
Maintaining consistent food production off-grid presents unique challenges. Pest and disease control, unpredictable weather patterns, and the need for efficient water management are significant concerns. Solutions include employing integrated pest management techniques (IPM), such as companion planting and natural predators, to minimize reliance on chemical pesticides. Diversifying crops reduces vulnerability to single-point failures. Implementing water harvesting techniques like rainwater collection and greywater recycling addresses water scarcity.
Careful crop selection, considering drought tolerance and disease resistance, is crucial. Furthermore, preserving harvested food through techniques like canning, drying, and fermentation extends shelf life and ensures food security throughout the year. For instance, a community garden utilizing shared resources and knowledge could help mitigate individual challenges.
Suitable Crops for Different Climates and Off-Grid Settings
Crop selection is paramount. In arid climates, drought-resistant crops like beans, squash, and certain varieties of corn are ideal. Temperate climates are suitable for a wider variety of crops, including leafy greens, root vegetables, and small fruits. Tropical climates offer opportunities for growing a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and even rice. Consider the nutritional value and yield potential of each crop.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out off grid living new york now.
For example, leafy greens provide essential vitamins and minerals, while root vegetables offer carbohydrates and storage potential. High-yield varieties are particularly important in off-grid settings where space may be limited.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Off-Grid Farming
Establishing a successful off-grid farm requires specific tools and equipment. Careful consideration of initial investment costs is essential.
The following list provides an overview of essential items and estimated costs (these are approximate and can vary significantly based on quality and location):
- Shovel & Hoe (approx. $50): Essential for soil preparation and weeding.
- Hand Trowel & Cultivator (approx. $30): Useful for smaller tasks and transplanting.
- Watering Can & Hose (approx. $50): For efficient irrigation, consider a rainwater harvesting system for reduced water costs.
- Seeds & Seedlings (approx. $100 – $200 annually): Varies based on crop selection and quantity.
- Basic hand tools (knives, pruning shears) (approx. $40): For harvesting and plant maintenance.
- Compost Bin (approx. $50 – $150): For creating nutrient-rich soil amendment.
Larger investments might include a greenhouse (approx. $500 – $2000) for extending the growing season or a simple irrigation system (approx. $200 – $1000) depending on scale and complexity.
Developing Off-Grid Businesses and Services: How To Make Money Off Grid Living
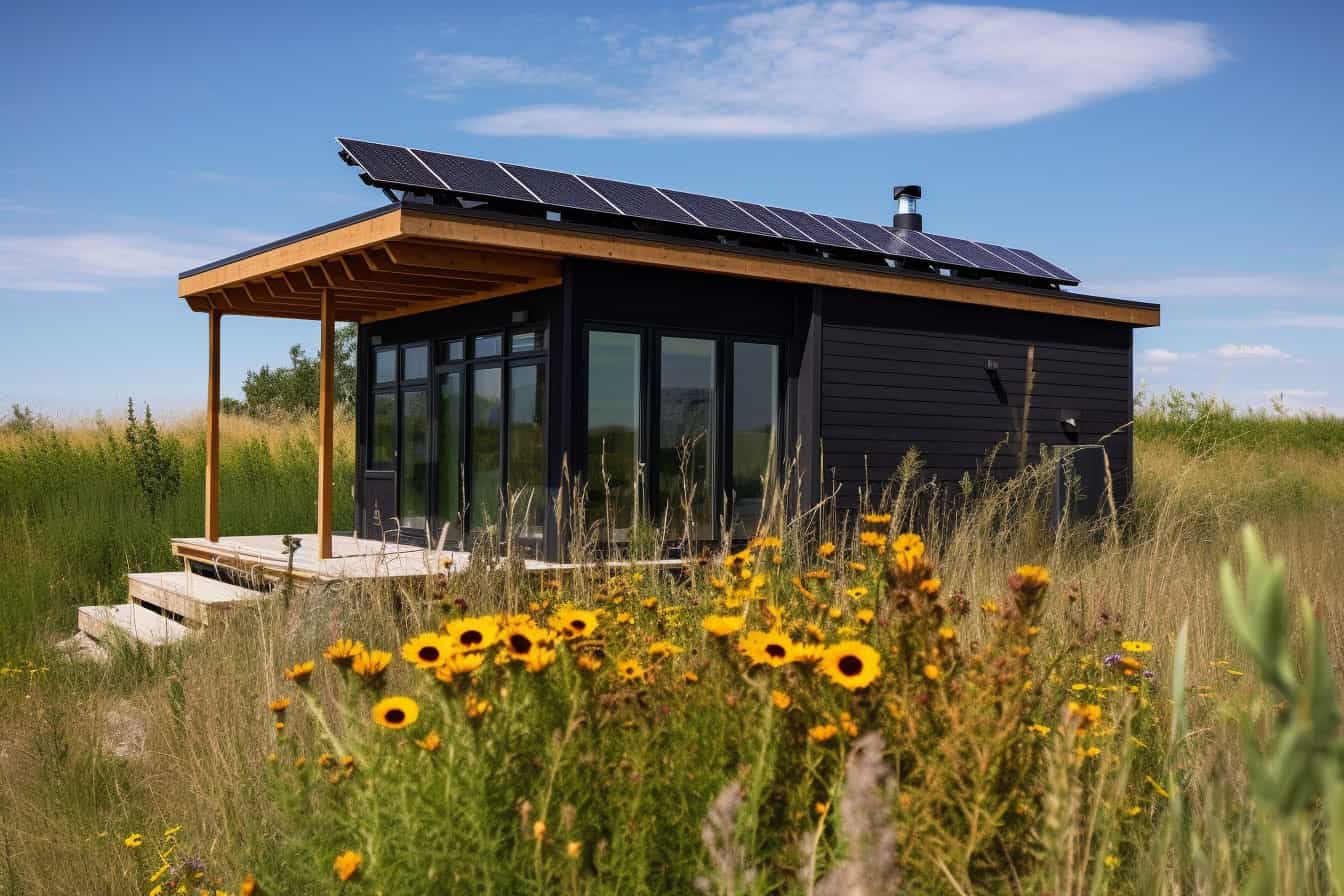

Embracing off-grid living doesn’t mean abandoning financial security. In fact, the unique lifestyle offers fertile ground for innovative and profitable businesses, capitalizing on the very aspects that define it: self-sufficiency, resourcefulness, and a connection to nature. By leveraging these strengths, you can create a thriving enterprise while maintaining your commitment to a sustainable, off-grid existence. This section explores the exciting possibilities of developing and running businesses in remote locations.
Profitable Off-Grid Business Examples
Several business models thrive in off-grid environments. Artisan crafts, for example, capitalize on the demand for unique, handcrafted goods, often made with locally sourced materials. Imagine a thriving online business selling exquisitely carved wooden bowls or hand-woven textiles, marketed directly to customers worldwide. Ecotourism offers another lucrative avenue. By offering guided nature walks, wildlife viewing tours, or unique accommodation in eco-friendly cabins, you can tap into the growing market of environmentally conscious travelers seeking authentic experiences.
Finally, remote consulting allows you to leverage your existing skills and expertise, offering services like web design, writing, or virtual assistance to clients across the globe, all while enjoying the peace and quiet of your off-grid haven. The key is to identify skills and passions that translate well into a remote business model, catering to a market that values authenticity and sustainability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Off-Grid Businesses
Running a business off-grid presents both unique advantages and challenges. On the positive side, lower overhead costs (reduced rent, utilities) and a slower pace of life can contribute to improved work-life balance and potentially higher profit margins. The unique selling proposition of an off-grid location can also attract customers seeking authentic experiences. However, challenges include limited access to reliable internet, potential supply chain issues, and difficulties in attracting and retaining employees.
Furthermore, obtaining necessary permits and licenses can be more complex in remote areas, and marketing and distribution might require more creative solutions. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for success.
Creating a Business Plan for an Off-Grid Enterprise
A well-structured business plan is essential for any successful venture, particularly in the unique context of off-grid living. This plan should include:
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of your business, its goals, and its market.
- Company Description: Details about your business structure, mission, and values.
- Market Analysis: Research into your target market, competition, and pricing strategies.
- Organization and Management: Details of your business structure and team.
- Service or Product Line: A description of what you offer and how it meets market needs.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Your plan to reach your target market and generate sales.
- Financial Projections: Detailed financial forecasts, including startup costs, revenue projections, and profitability analysis.
- Funding Request (if applicable): A clear Artikel of your funding needs and how you plan to secure them.
- Appendix: Supporting documents, such as market research data or resumes of key personnel.
This comprehensive approach will provide a roadmap for navigating the complexities of building a successful off-grid business. Remember to adapt your plan to the specific challenges and opportunities presented by your chosen location and business model.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Off-Grid Businesses
Navigating the legal landscape of off-grid entrepreneurship requires careful planning and attention to detail. The specific regulations will vary depending on your location, but some common considerations include:
| Aspect | Considerations | Potential Issues | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Licensing | Obtain necessary permits and licenses to operate legally. | Operating without proper licenses can result in fines or closure. | Thoroughly research local regulations and apply for licenses well in advance. |
| Zoning and Land Use | Ensure your business complies with local zoning laws and land use regulations. | Violations can lead to legal action and business disruption. | Consult local authorities to ensure compliance before starting operations. |
| Environmental Regulations | Comply with environmental protection laws, especially regarding waste disposal and resource management. | Environmental damage can result in significant penalties. | Implement sustainable practices and seek advice from environmental agencies. |
| Tax Obligations | Understand and comply with all relevant tax laws, including income tax, sales tax, and property tax. | Failure to pay taxes can lead to serious financial penalties. | Consult a tax professional to ensure compliance with all applicable tax regulations. |
Monetizing Off-Grid Skills and Expertise

Embracing a self-sufficient lifestyle doesn’t mean sacrificing financial stability. In fact, the skills you develop living off-grid are often highly valuable and marketable, offering unique opportunities to generate income while maintaining your chosen way of life. This section explores how to transform your off-grid expertise into a profitable venture.Many off-grid skills translate directly into marketable services and products.
The key is recognizing the demand for these skills and effectively connecting with potential clients. By strategically marketing your abilities and building a strong online presence, you can create a sustainable income stream that supports your off-grid existence.
Valuable Off-Grid Skills and Their Market Potential
Numerous skills honed through off-grid living are in high demand. Carpentry, for example, is always needed for building and repairs, both in rural and urban settings. Similarly, mechanical skills, particularly those relating to the maintenance and repair of off-grid power systems (solar, wind, etc.), are highly sought after. Herbalism, with its focus on natural remedies and sustainable practices, is gaining significant popularity, offering opportunities in product creation and consultation.
Other valuable skills include sustainable agriculture, water management, and permaculture design. These skills can be monetized through various avenues, such as offering workshops, creating and selling handcrafted products, or providing consulting services.
Marketing and Selling Off-Grid Products and Services
Effectively marketing your off-grid skills requires a multi-pronged approach. Word-of-mouth referrals within your local community are invaluable. Participating in local farmers’ markets or craft fairs provides direct access to potential customers. Online platforms like Etsy, Shopify, and specialized forums dedicated to off-grid living offer wider reach. Creating a professional website showcasing your skills and services is crucial for building credibility and attracting clients.
High-quality photography and compelling descriptions of your products or services are essential. For example, showcasing beautifully crafted wooden furniture with detailed descriptions of the sustainably sourced materials and the craftsmanship involved can significantly enhance your appeal.
Networking and Building Relationships within the Off-Grid Community
The off-grid community is a valuable resource for both support and business opportunities. Attending workshops, conferences, and local gatherings provides opportunities to network with like-minded individuals and potential clients. Collaborating with other off-grid entrepreneurs on joint projects can expand your reach and diversify your income streams. Building strong relationships based on trust and mutual respect is crucial for long-term success.
For instance, a carpenter might collaborate with a permaculture designer to offer complete sustainable building packages, combining their complementary skills to attract a wider client base.
Creating a Compelling Online Presence
A well-designed website and active social media presence are essential for attracting clients. Your website should clearly showcase your skills, services, and testimonials. High-quality images and videos demonstrating your work are crucial. Social media platforms like Instagram and Facebook can be used to share your work, engage with potential clients, and build your brand. Consider running targeted advertising campaigns to reach specific demographics interested in off-grid living or sustainable practices.
For example, a mechanic specializing in solar panel repair could create engaging videos demonstrating common repairs and showcasing their expertise, driving traffic to their website and generating leads.
Financial Planning and Resource Management for Off-Grid Living
Embarking on an off-grid lifestyle requires meticulous financial planning and resource management. Unlike conventional living, where access to resources and services is readily available, off-grid existence demands a proactive and comprehensive approach to budgeting, saving, and resource utilization to ensure financial stability and long-term sustainability. Failure to adequately plan financially can quickly lead to hardship and compromise the very independence off-grid living aims to achieve.
Creating a Comprehensive Off-Grid Budget, How to make money off grid living
A detailed budget is the cornerstone of successful off-grid living. This budget must encompass all anticipated expenses, from initial setup costs (land acquisition, building materials, initial equipment) to ongoing operational expenses (food, fuel, maintenance, healthcare). It’s crucial to accurately estimate these costs, factoring in potential unforeseen expenses and seasonal variations. For example, heating costs will be significantly higher in colder climates, while water sourcing may require more investment in drier regions.
Income streams, whether from remote work, agricultural production, or craft sales, must also be meticulously accounted for. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the budget based on actual spending and income is essential for maintaining financial control.
Strategies for Managing Finances and Resources in Remote Settings
Managing finances and resources in a remote location presents unique challenges. Access to traditional banking services may be limited, necessitating alternative financial strategies. This might involve utilizing online banking platforms, establishing relationships with local credit unions, or employing cash-based systems for smaller transactions. Resource management requires careful planning and conservation. Strategies such as rainwater harvesting, composting toilets, and efficient energy generation (solar, wind) are essential for reducing reliance on external resources and minimizing expenses.
Regular maintenance of equipment and infrastructure is crucial to prevent costly repairs or replacements down the line. For instance, a well-maintained solar panel system will generate power for years, while neglecting it could lead to significant repair bills or even system failure.
Diversifying Income Sources for Financial Stability
Relying on a single income stream in an off-grid setting is risky. Diversification is key to building financial resilience. Multiple income sources can mitigate the impact of unexpected events, such as crop failure or equipment malfunction. Examples include combining agricultural production with freelance work, selling handcrafted goods online, offering off-grid consulting services, or generating income through sustainable tourism (if appropriate for the location).
This strategy ensures a more stable financial foundation, even if one income stream experiences a downturn. For instance, if a farmer experiences a poor harvest, income from online sales of handcrafted goods can help offset the loss.
Essential Financial Considerations Before Transitioning to Off-Grid Living
Before making the transition, a thorough assessment of financial preparedness is vital.
- Emergency Fund: Establish a substantial emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses or periods of reduced income.
- Debt Reduction: Minimize existing debts to reduce financial burdens and free up resources for off-grid investments.
- Healthcare Coverage: Secure appropriate healthcare coverage, considering the limitations of access in remote areas.
- Initial Capital: Accumulate sufficient capital to cover initial setup costs and living expenses during the transition period.
- Long-Term Financial Plan: Develop a comprehensive long-term financial plan that Artikels income projections, expense management, and contingency strategies.
Visualizing Off-Grid Living and Income Generation
Embracing off-grid living doesn’t mean sacrificing comfort or financial stability. By carefully planning and visualizing your self-sufficient homestead and income-generating ventures, you can create a life that is both fulfilling and financially rewarding. This section will paint a picture of a thriving off-grid existence, highlighting the practical aspects and the aesthetic appeal of such a lifestyle.
A Self-Sufficient Off-Grid Homestead
Imagine a picturesque homestead nestled amongst rolling hills or beside a tranquil lake. The air is clean and crisp, the sounds of nature providing a constant, calming soundtrack. This homestead is entirely self-sufficient, a testament to careful planning and sustainable practices. The primary energy source is a combination of solar panels, strategically positioned to maximize sun exposure, and a wind turbine, harnessing the power of the wind.
These renewable energy sources power the home, providing electricity for lighting, appliances, and a small workshop. Water is sourced from a well, purified using a multi-stage filtration system, and stored in a large rainwater harvesting tank. Greywater recycling systems minimize water usage and support the garden.The agricultural practices are centered around permaculture principles. Raised garden beds, filled with rich compost, support a diverse range of vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
A small orchard provides apples, pears, and cherries, while chickens roam freely, providing fresh eggs and helping to manage pest control. The aesthetic is one of natural beauty, with winding paths, strategically placed trees providing shade, and a small pond attracting wildlife. The overall feeling is one of peace, tranquility, and a deep connection with nature. The homestead is visually appealing, a testament to thoughtful design and integration with the surrounding environment.
The home itself is built with locally sourced, sustainable materials, blending seamlessly with the landscape. A small greenhouse, nestled against the south-facing wall of the house, extends the growing season and allows for year-round cultivation of certain crops.
Layout of a Small-Scale Off-Grid Business
Consider a small-scale woodworking business operating from a repurposed barn. The barn, painted a warm, inviting shade of natural wood stain, is equipped with solar-powered lighting and tools. The layout prioritizes efficiency, with a designated area for raw materials, a workspace with several woodworking benches and power tools, and a separate area for finishing and packaging. The tools are neatly organized and well-maintained, reflecting a commitment to quality craftsmanship.
A small office area, equipped with a computer and internet access (via satellite or a robust cellular connection), handles orders and customer communication. The space is clean, well-lit, and organized, reflecting both practicality and a dedication to creating high-quality products. The visual appeal is rustic charm meets modern functionality, creating a workspace that is both efficient and aesthetically pleasing.
The finished products, perhaps handcrafted furniture or custom-made cabinetry, are displayed in a designated area, showcasing the quality and craftsmanship. This visual presentation serves as a powerful marketing tool, attracting potential customers and demonstrating the value of the handcrafted items.
Embracing off-grid living doesn’t mean sacrificing financial security; it means redefining it. By strategically combining sustainable practices, innovative business models, and sound financial planning, you can create a life that is both rewarding and financially stable. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge and inspiration to embark on your own off-grid adventure, transforming your dreams of self-sufficiency into a tangible reality.
Remember, the journey is as enriching as the destination – so embrace the challenge, embrace the freedom, and embrace the possibilities that await you in the world of off-grid living.